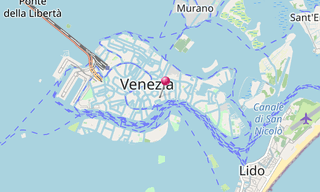
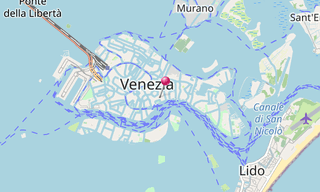
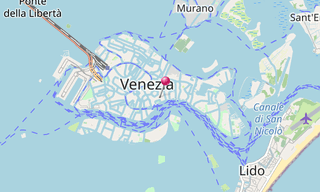
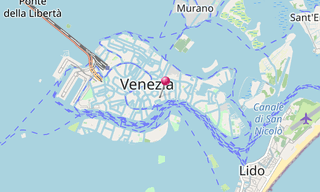
The Venetian Lagoon (Laguna di Venezia) is an enclosed bay of the Adriatic Sea, in northern Italy, in which the city of Venice is situated. Its name in the Italian and Venetian languages, Laguna Veneta of Latin lacus, “lake” has provided the English name for an enclosed, shallow embayment of salt water, a lagoon.
The Venetian Lagoon stretches from the River Sile in the north to the Brenta in the south, with a surface area of around 550 km². It is around 8% land, including Venice itself and many smaller islands. About 11% is permanently covered by open water, or canal, as the network of dredged channels are called, while around 80% consists of mud flats, tidal shallows and salt marshes. The lagoon is the largest wetland in the Mediterranean Basin.
.hero.landscape.jpg)

.hero.jpg?w=320)
.hero.jpg?w=320)
.hero.jpg?w=320)
.hero.jpg?w=320)
.hero.jpg?w=320)
.hero.jpg?w=320)
.hero.jpg?w=320)
.map.png)